For ActLight, this year’s CES event in Las Vegas highlights the increasing significance of light sensors in diverse industries, including consumer electronics, healthcare, industrial applications, and scientific research. Light sensors are driving innovations that redefine how we live, work, and interact with the world.
A photosensor, also known as a photosensitive sensor or a light sensor, is a device that detects and measures the presence and intensity of light. It converts the light energy into an electrical signal, and have become an integral part of our technological world.
The future of the photosensor market looks even more promising. with the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) and smart cities, the demand for photosensors is expected to increase significantly; they are now poised to play a much more transformative role in shaping the future of technology from smart lighting systems that adjust based on natural light levels, to security systems that detect motion and presence. Further, there is a growing focus on energy conservation and sustainability likely to drive the adoption of photosensors in green buildings and renewable energy systems.
Transforming Healthcare and Beyond
The impact of light sensors extends far beyond consumer electronics, revolutionizing healthcare, industrial applications, and scientific research. In healthcare, light sensors are used in a variety of medical devices, from pulse oximeters that measure blood oxygen saturation to spectrophotometers that analyze blood samples. They are also employed in laser therapy devices that treat various medical conditions.
In the industrial sector, light sensors are playing a pivotal role in enhancing safety and efficiency. From proximity detection and obstacle avoidance systems in industrial machinery to motion-activated lighting and security alarms in manufacturing facilities, light sensors are transforming the way industrial processes are managed and safeguarded.
In scientific research, light sensors are enabling groundbreaking discoveries in fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics. From studying the behavior of cells and molecules to measuring environmental parameters, light sensors are providing scientists with new tools and insights to advance our understanding of the world around us.
Photosensors can be integrated into a wide range of IoT devices, from smart lighting systems that adjust based on natural light levels, to security systems that detect motion and presence. Additionally, the growing focus on energy conservation and sustainability is likely to drive the adoption of photosensors in green buildings and renewable energy systems.
“As we look to the future, the potential of light sensors is limitless and our DPD meets company pain-points.”
As CEO Serguei Okhonin states, the potential is limitless, however there are new pain points that companies are facing today:
Limited Precision
Pain Point: Traditional light sensors are limited in their sensitivity and dynamic range. This makes them difficult to use in applications where they need to accurately measure light levels over a wide range of conditions.
Solution: Tomorrow’s light sensors will have significantly improved sensitivity and dynamic range. This will allow them to be used in a wider range of applications, such as:
- Automotive: Improved light sensors can be used for automatic headlights, lane departure warnings, and other safety features.
- Healthcare: Improved light sensors can be used for pulse oximeters, spectrophotometers, and other medical devices.
- Industrial: Improved light sensors can be used for proximity detection, obstacle avoidance, and other industrial applications.
Energy-intensive Sensors
Pain Point: Traditional light sensors are power-hungry. This makes them difficult to use in battery-powered devices.
Solution: Tomorrow’s light sensors will be much more power-efficient. This will allow them to be used in a wider range of battery-powered devices, such as:
- Wearables: Improved light sensors can be used for health monitoring, fitness tracking, and other wearable applications.
- Smartphones: Improved light sensors can be used for automatic brightness adjustment, gesture control, and other smartphone features.
- Home automation: Improved light sensors can be used for motion-activated lights, smart thermostats, and other home automation devices.
- Sustainability: the increasing focus on sustainable solutions is driving the development of photosensors that are energy-efficient and eco-friendly.
Bulky and Expensive Sensors
Pain Point: Traditional light sensors are bulky and expensive. This makes them difficult to integrate into small and affordable devices.
Solution: Tomorrow’s light sensors will be much smaller and more cost-effective. This will allow them to be used in a wider range of devices, such as:
- Medical devices: Improved light sensors can be used for minimally invasive surgery and other medical applications.
- Consumer electronics: Improved light sensors can be used for augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and other consumer electronics applications (smartphones, wearables).
- Robotics: Improved light sensors can be used for autonomous robots and other robotics applications.
Inaccurate sensors
Pain Point: Traditional light sensors are not very accurate. This can lead to errors in measurement and applications.
Solution: Tomorrow’s light sensors will have significantly improved accuracy. This will allow them to be used for a wider range of applications with greater precision, such as:
- Consumer electronics: Inaccurate gesture control can make it difficult to interact with devices, as the gestures may not be recognized correctly, leading to users giving up on using gesture control features altogether.
- Environmental monitoring: Improved light sensors can be used to measure air quality, pollution levels, and other environmental parameters.
- Scientific research: Improved light sensors can be used for a wide range of scientific research applications, such as studying the behavior of cells and molecules.
ActLight leads the technological revolution, dedicated to advancing light sensing technology and tackling these pain points as part of our core values. With our distinctive IP portfolio, notably ActLight’s Dynamic PhotoDetector technology, we have a robust foundation to create innovative solutions which meets our customers’ evolving needs.
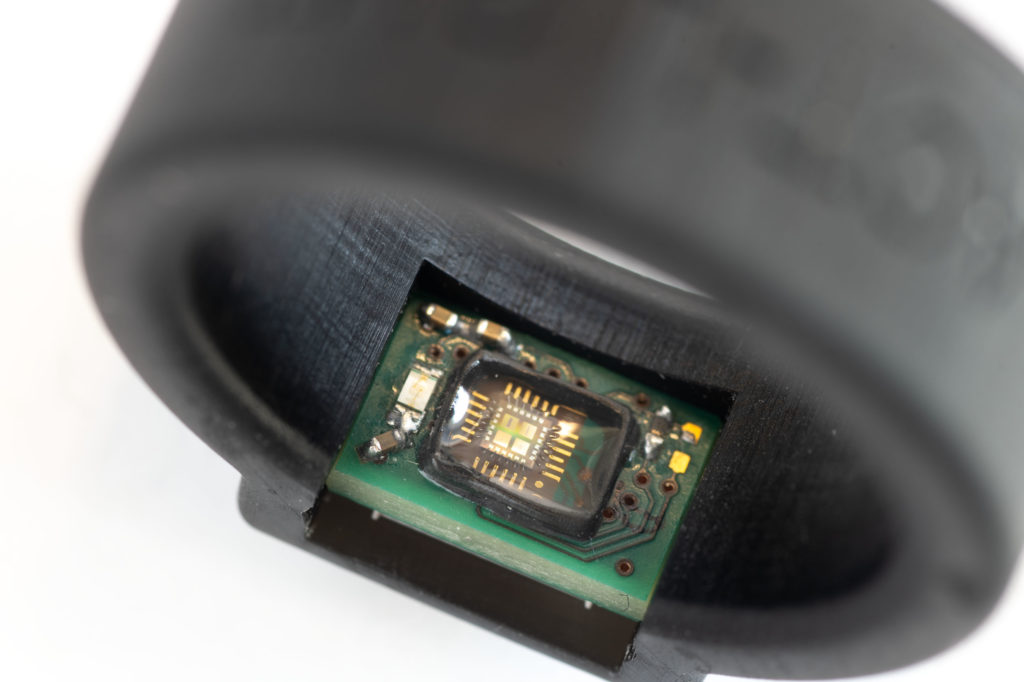

We are excited to be part of this transformative journey and to see how light sensors continue to shape the future of technology, illuminating the path towards a more connected, intelligent, and sustainable world.
Connect with us on LinkedIn!






